[Spring6.0源码解析]简述@Configuration注解
@Configuration 标注在类上,启动 Spring 会自动扫描@Configuration注解的类,将其注册到IOC容器并实例化bean对象。如果在@Configuration注解的类中使用@Bean注解某个类对象的方法,Spring也会自动将注解了@Bean的方法注册到IOC容器,并进行实例化。
注解源码
@Configuration 注解本质上是个 @Component 注解,所以被 @Configuration 标注的类会被注册到IOC,且可以被 @ComponentScan 注解扫描到。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
/**
* 存入到Spring IOC容器中的ID
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
String value() default "";
/**
* 表示被@Configuration注解的类是否被代理,以及配置类中被@Bean注解的方法生成的Bean
* 在IOC容器中是否为单例对象
*
* true:full全局模式(默认)
* false:lite轻量级模式
*
* full全局模式,被@Configuration注解的配置类会被代理(CGLIB实现),配置类中被@Bean
* 注解的方法生成的Bean在IOC容器中是单例模式。也就是说,无论调用多少次被@Bean标注的
* 方法,返回的都是同一个bean对象。
*
* lite轻量级模式,被@Configuration注解的配置类不会被代理,配置类中被@Bean注解的方法
* 生成的Bean在IOC容器中也不是单例模式。也就是说,每次调用被@Bean注解标注的方法时,都会
* 返回一个新的Bean对象。
*
* @since 5.2(Spring 5.2版本加入)
*/
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
/**
* 表示使用@Bean注解标注的方法是否需要唯一的方法名。
*
* true:使用@Bean注解标注的方法具有唯一方法名称,且方法名称不会重叠
* false:使用@Bean注解标注的方法不唯一,存在重叠风险
*
* 默认为true。
*
* @since 6.0(Spring 6.0版本加入)
*/
boolean enforceUniqueMethods() default true;
}
使用场景
当某个类被@Configuration注解标注时,说明这个类是配置类。可以在这个类中,使用@Bean注解,向IOC容器中注入Bean对象;也可以使用 @Autowrite、@Resource、@Inject等注解来注入所需要的Bean对象。
另外,在使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 类创建IOC容器事,需要注意两点:
- 如果使用传入 Class 入参的构造函数,则传入Class的配置类上的
@Configuration可以省略,但是如果省略@Configuration,每次调用配置类中被@Bean标注的方法时,都会返回不同的 Bean 实例对象。 - 如果使用传入 String 入参的构造函数,表示传入应用程序的包名来创建 IOC容器,则配置类上的
@Configuration不可以省略。
两种构造方法如下:
/**
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext, deriving bean definitions
* from the given component classes and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param componentClasses one or more component classes — for example,
* {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
register(componentClasses);
refresh();
}
/**
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext, scanning for components
* in the given packages, registering bean definitions for those components,
* and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param basePackages the packages to scan for component classes
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(String... basePackages) {
this();
scan(basePackages);
refresh();
}
使用案例
准备代码
- 一个用于注册到IOC的类:
public class Person {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
- 配置类
@Configuration
public class ConfigurationAnnotationConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
- 启动类
public class ConfigurationAnnotationTest {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ConfigurationAnnotationTest.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigurationAnnotationConfig.class);
ConfigurationAnnotationConfig config = context.getBean(ConfigurationAnnotationConfig.class);
Person person1 = config.person();
Person person2 = config.person();
LOGGER.info("person1 是否等于 person2 ===>> {}", (person1 == person2));
}
}
proxyBeanMethods的使用
在之前提到,proxyBeanMethods配置表示用 @Bean 注解的方法在IOC容器中是否为单例对象,默认为true。
默认情况下,打印出结果如下:
person1 是否等于 person2 ===>> true
修改一下proxyBeanMethods的值为false:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class ConfigurationAnnotationConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
打印结果如下:
person1 是否等于 person2 ===>> false
从输出结果可以看出,当@Configuration中的proxyBeanMethods属性为false时,每次调用@Configuration注解标注类中被@Bean标注的方法时,都会返回不同的Bean实例对象。
创建IOC容器
传入配置类
调用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类的构造方法传入配置类的Class对象创建IOC容器时,可以省略配置类上的@Configuration注解,如下:
public class ConfigurationAnnotationConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
输出结果:
person1 是否等于 person2 ===>> false
可以看到,若省略配置类上的@Configuration注解,则每次调用配置类中被@Bean注解标注的方法时,都会返回不同的Bean实例对象,与@Configuration中设置proxyBeanMethods的属性为false的效果相同。
传入包
调用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类的构造方法传入包名创建IOC容器时,不能省略配置类上的@Configuration注解:
public class ConfigurationAnnotationConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
执行函数:
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("io.binghe.spring.annotation.chapter01.configuration");
ConfigurationAnnotationConfig config = context.getBean(ConfigurationAnnotationConfig.class);
Person person1 = config.person();
Person person2 = config.person();
LOGGER.info("person1 是否等于 person2 ===>> {}", (person1 == person2));
}
此时运行main方法,会发生报错:
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'io.binghe.spring.annotation.chapter01.configuration.config.ConfigurationAnnotationConfig' available
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:340)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:331)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1148)
at io.binghe.spring.annotation.chapter01.configuration.ConfigurationAnnotationTest.main(ConfigurationAnnotationTest.java:36)
添加上@Configuration注解则程序执行正常。
扩展知识
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
Spring在 BeanFactory 的基础上提供一些具体容器的实现。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext就是一个用来管理注解 Bean 的容器。如下结构图:
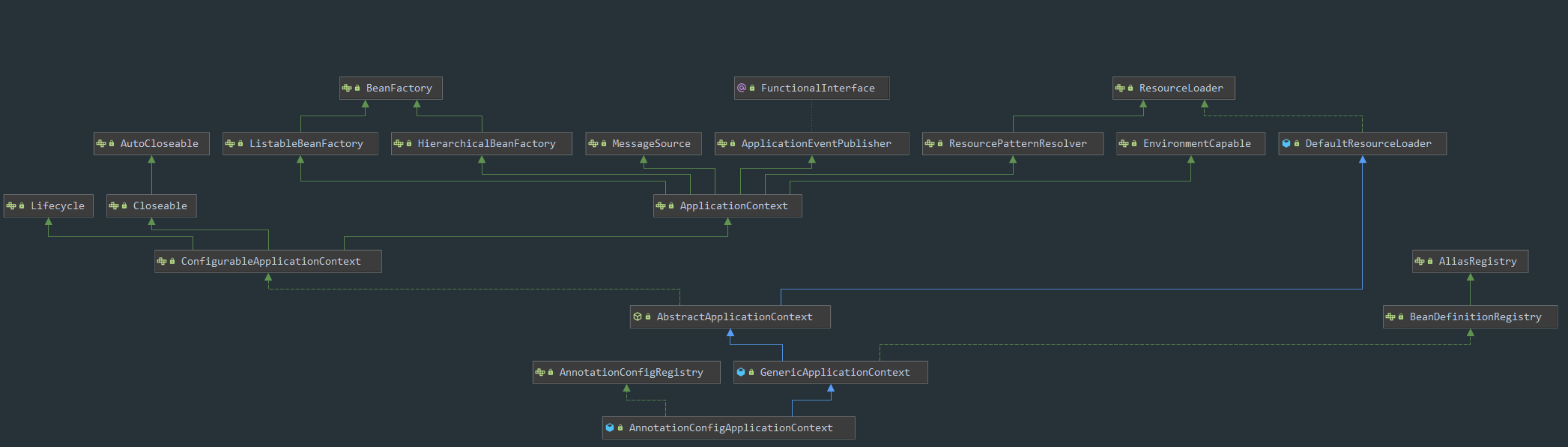
从图中可以看到,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext继承GenericApplicationContext(通用应用上下文),而GenericApplicationContext又实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,所以可以通过AnnotationConfigApplicationContext实例类注册BeanDefintion,然后调用refresh()方法来初始化上下文。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext还继承了AbstractApplicationContext,而AbstractApplicationContext提供了ApplicationContext的抽象实现
热门相关:超武穿梭 第一神算:纨绔大小姐 这里有空房间吗 天启预报 寂静王冠